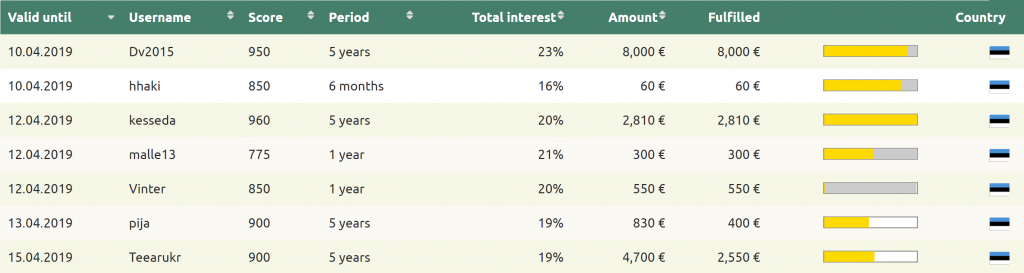
Balance sheet lending or portfolio lending is a type of borrowing that involves a loan in which the lender retains the debt throughout the term of the loan. In other types of lending, the lender may sell the debt at a reduced price, particularly if the borrower fails to pay. However, in balance sheet lending, this is not allowed and the original lender retains the rights over the debt and cannot sell it to the third party throughout its cycle.
Balance sheet lending is pretty much similar to peer to peer lending. However, the difference comes in terms of risk structure if a loan defaults. In p2p lending, the platform connects the borrower and the lender; in contrast, balance sheet lending lends the money to a borrower, which means the platform is directly liable in case the loan goes bad. For this reason, balance sheet lending can take different forms, but the underlying feature is that the platform provides a loan to borrowers on their own risk.
Some borrowers prefer balance sheet lending over p2p lending as they would rather deal with the original lender in case a problem develops during the life cycle of the loan.
Balance sheet lenders usually focus on specialized lending, including subprime short terms loans, POS loans, cash installments, factoring, and merchant cash advances.
How does balance sheet lending work?
In balance sheet lending, lenders are supposed to buy their money beforehand. The money might come from a wide range of sources including family offices, financial markets, and investment banks.
These loans usually go through a number of hands before it is disbursed to the borrower, which each clipping the ticket throughout its way. For this reason, the resulting loan becomes pretty much expensive for the lender, and therefore, the lender will pass the costs off to the borrower as well as the margin required to offset any losses they are accountable for.
This can essentially lead to high APRs for unsecured business loans.
Balance Sheet Lending vs. P2P Lending
Balance sheet lending is very similar to p2p lending or marketplace lending. However, there are still differences between the two.
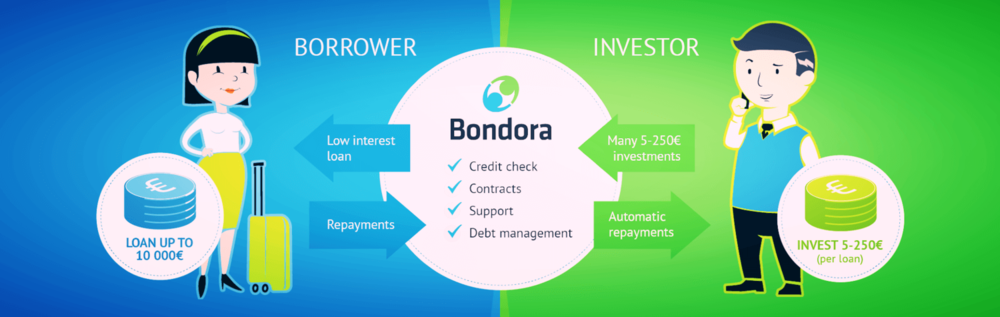
Peer to peer lending or p2p lending is an alternative funding option that enables borrowers to obtain money from individual lenders instead of banks and credit unions.
To understand which is the best option for your needs, I have compiled the differences between the two lending options.
Cost
Balance sheet – the cost required to cover the operation as well as the cost of obtaining the money is are passes off to the borrower, but prices can vary.
P2P lending- investors don’t have to pay to get the money back, or concern about the pricing risk to shield their losses. as a result, the investors take the return and the risk.
The funding process
Balance sheet – funds are readily availed once the application is approved.
P2P lending – the funds may be funded instantly or may go through some funding period. On some occasions, p2p platforms would struggle to balance the funds offered by the investors with the funds demanded by the borrowers, which can result in a prolonged funding period.
Risk structure
Balance sheet – in this type of lending, the lender carries all the risk for any losses.
P2P lending – in p2p, lenders take on risk when investing in specific loans, thus why they diversify their risk across a number of loans and even platforms.
Advantages of balance sheet lending
Balance sheet lending has several advantages, including:
-
Easy to manage
Working with only the original lender is easier for borrowers, unlike when the debt is transferred to another hand which can result in changes in rules.
-
Lower risk
Borrowers can reduce the risk in balance sheet lending since they are not required to place any item on the balance sheet as the item is not considered as an asset or liability.
-
Direct communication with the investor
In case of any problems, the borrowers can speak directly with the original investor/lender. In traditional lending, this may not be possible as the original lender may sell your loan to a third party, which also may sell the loan to another party, make it complicated to communicate.
-
Rapid company expansion
Loans obtained from balance sheet lending are typically used to help the business expand its operations. This may be to purchase production materials or covering the cost of labor, create a new line of products or opening a new branch.
Why lenders may opt to invest in balance sheet lending
Most investors in balance sheet lending are banks and investment institutions with a storied history and experience in their industry. The companies and banks have deep pockets and are in a pretty good position to take the risks that balance sheet loan demands.
Due to their financial muscles, these lenders can grow a wide pool of these loans. Moreover, they may also provide a large amount of these loans to a large number of borrowers, helping reduce their risk while increasing security through diversity.
The future of balance sheet lending
The business model of balance sheet lending can be referred to as an ideal type, meaning that the characteristics described are of this model in its pure form. The market for balance sheet lending, just like p2p lending, is still very young and in rapid growth, so the forecast of the development of the market is at present, very speculative.