Digital worlds or metaverses are not a new phenomenon. Millennials and Gen Z have spent a large portion of their lives in digital universes created by massively multiplayer online games (MMOs) such as Fortnite. The reach of the metaverse, however, goes beyond gaming. Video games and their social functions are examples of metaverse components.
The metaverse is an interconnected virtual world where people will create, work, play, socialise and transact in a fully functioning economy that rivals the physical world.
It is such a phenomenal prospect that for the first time in recent history, all tech giants are tussling over one business territory; metaverse building. Apple has dominated the mobile operating systems market, while Google was happy with its search engine dominance.
Microsoft and Amazon were happy to share the cloud computing pie while Facebook and Google minted their cash off online advertising. However, all that has changed as all tech titans, alongside Asian giants such as Tencent Holdings, stake their claim on the virtual and augmented reality technology market.
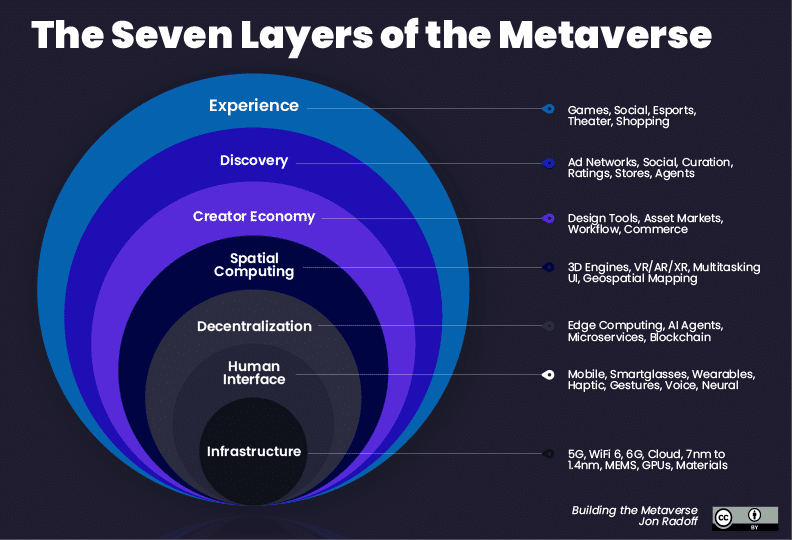
Figure: AI potential applications in the metaverse (source: jradoff.medium)
Businesses building metaverse components
Tencent dominates China’s super app market via WeChat. WeChat has over 1.26 billion users. Tencent has a wide array of mobile games and is China’s leading game publisher. It has also invested in other international game studios.
Tencent is now purchasing Black Shark, a gaming-oriented hardware startup founded by Xiaomi for $2 billion. Black Shark is going the Oculus route and will produce AR and VR headsets. Black Shark is, therefore, Tencent’s metaverse building arm that will augment its video game world building investments in Roblox and Unreal Engine platforms.
On the other hand, Apple is facing a slight delay on its virtual reality and mixed augmented headsets development plans.
To lead the metaverse development race, Mark Zuckerberg of the now Meta brand is bankrolling its development with over $10 billion worth of funds via its Reality Labs division. Reality Labs is Meta’s metaverse components software and hardware development division.
The Meta CEO has predicted that the metaverse is the next phase of growth on the internet, calling it a ‘social version of home’. The Mark Zuckerberg metaverse has Horizon Worlds, a metaverse component that already has 300,000 users.
Horizon Worlds is Meta’s biggest bet. It is a social virtual reality platform powered by its Quest headsets. One of Horizon Worlds’ metaverse components is Horizon Venues; a VR live events platform. Horizon Workrooms is its virtual reality conferencing space that functions via a unique invite system. Meta plans to invest at least $180 billion into the Metaverse in the coming decade.
Microsoft, however, has some of the best fleshed out metaverse plans of all tech giants. For example, meta might entice billions of WhatsApp, Instagram, and Facebook users into its metaverse. Microsoft, however, has functional gaming worlds and is well in on its metaverse domination plans.
Gaming is one of the most potent on-ramps to the metaverse ecosystem, and Microsoft is an old hand in the video gaming industry. It has built a huge gamer fanbase from early PC games such as Doom and the latest Xbox releases such as Halo Infinite and the upcoming Lego Star Wars: The Skywalker Saga.
Microsoft also purchased Minecraft in 2015. Minecraft has one of the most potent worldbuilder ecosystems. It has over 140 million users each month, and its mini metaverse is a direct competitor to Roblox.

Figure: Second Life (source: Second Life)
Then in January 2022, the multinational technology corporation announced its intention to acquire Activision Blizzard for a massive $68.7 billion. Activision Blizzard owns popular video game titles such as Call of Duty, Diablo, WarCraft, and OverWatch.
Activision’s game titles are cross platform and available on Nintendo, PlayStation, and Xbox Game Pass. Consequently, Activision Blizzard’s 371 million monthly active users will become sticky Xbox Game Pass users.
To this end, if traditional gaming franchises are the on-ramps to metaverses that most pundits say that they are, then Microsoft may stand a chance of breakout success against Tencent’s and Sony’s massive video gaming strongholds.
In contrast, Meta does not have many gaming initiatives for its metaverses. Facebook only has Farmville in its gaming arsenal, perhaps embracing the Second Life’s virtual space proto metaverse building strategy.
Second Life is a social network with life simulation metaverse components. It is a unique social hub that has a virtual economy. Unlike gaming metaverses, Second Life does not have an overarching conflict driven storyline.
Members come to Second Life to chill out and indulge in pressure-free fun activities. It is, therefore, possible that in the end, metaverse users will use Quest headsets to access the metaverse VR experiences.
These users will then turn to the game and virtual world ecosystems such as World of WarCraft, Roblox, Second Life or blockchain technology’s Axie and Decentraland to play, socialise, create, work and transact. That said, the metaverse is still in its formative stages, and it is unclear how the Web3 evolution will flesh it out.
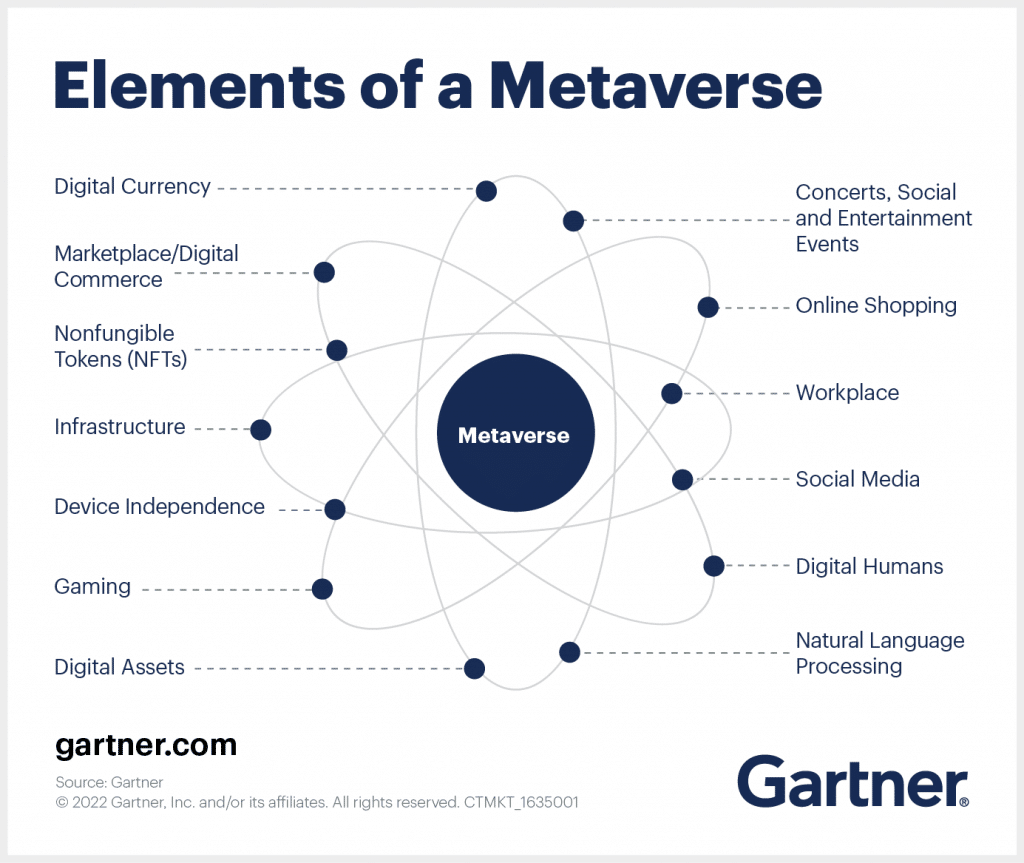
Figure: Elements of a Metaverse (source: Cryptostars)
Main metaverse components
However, the metaverse will be persistent, live, and synchronous. It will be a living, consistent experience for all its users in real-time. Any person from any corner of the globe will join the open metaverse and participate in its activity either individually or socially.
The metaverse will also have a functioning economy, where users can eke out a living in its digital labour processes. It could have more commercial activity than the current web and will have a greater reach and economic upside.
The metaverse will also change the monetisation and allocation of modern resources. For example, the work from home labourer will participate in virtual labour and earn their high-value wage from its borderless economy. Below are some core metaverse components that will function together to form the metaverse.
Virtual worlds, games and communities

Figure: Meta virtual world announcement (source: CNET)
Pundits predict that virtual worlds are the next evolutionary step in social media platforms. For this reason, tech giants such as Meta and Microsoft are making headways into virtual world-building as an actionable rather than a futuristic vision.
There has been a rising interest in virtual worlds during and after the pandemic as more people find social comfort in their game-like environments. Minecraft, Roblox and Fortnite have some of the most spruced up virtual worlds, and more startups are investing in next generation non-game related complex digital societies.
Second Life, for instance, has had a functional virtual world since 2003. It has a dedicated and loyal resident community as well. Second Life had millions of users and boatloads of media attention in its halcyon days.
In 2006, Adidas spent over a million dollars on Second Life, setting up an A3 Micro ride trainer virtual trainer shop. Second life users could purchase these trainers and give their avatars an extra bounce on their step.
However, the Second Life novelty wore off as its expansion began to slow down. Most brands had ventured into Second Life to make sales, not create or engage. Consequently, when Second Life users, for instance, quit wearing the A3 Micro ride trainer since it was lagging the sim, Adidas quickly packed up and left.
That said, the leftover community has blossomed into a stable community of 90,000 plus users. Moreover, its Roblox-like framework is open-ended, meaning that the community content creation charts its development direction.
Communities are, therefore, a vital part of virtual world-building. Second Life is living proof that metaverse should be in the hands of the community if they are to grow sustainably.
Virtual and augmented reality
Figure: Microsoft HoloLens 2 (source: Microsoft)
Virtual and augmented reality (VR and AR) are developing technologies to infuse virtual worlds with a 3D experience. Virtual reality technology leverages software that teleports users to a virtual world.
It is a metaverse component with simulation and modelling features supporting 3D interaction with the environment. Virtual reality generates a virtual environment via gloves, sensors, and VR headsets.
It blends fictional visual elements into digital world creation and, in the future, will give its users physical simulations via VR technology and equipment. To illustrate this point, video games that leverage VR gives their gamers an immersive perspective of the action via headsets such as the HTC Vive or Oculus Rift.
VR headset use in gaming brought in $22.9 billion in revenue in 2020. However, the VR market will cross $209.2 billion as the VR device demand grows due to applications in virtual worlds, the military, sport, education, fashion, and medical sectors.
On the other hand, augmented reality utilises smart devices to augment real world experiences. For example, it places 3D images onto a digital device’s screen, making it appear as if that digital object is in the same space as its observer.
Tech firms such as Microsoft and Google are creating 3D communication technology that turns users into life size holograms. Google’s Project Starline, for instance, allows its users to enjoy life size 3D hologram face to face chats.
Columbia Shipmanagement Ltd, on the other hand, had its CEO Mark O, Neil appear in 3D form at a Manila conference. The firm wants to use AR technology in its remote worker training process.
Artificial intelligence (AI)
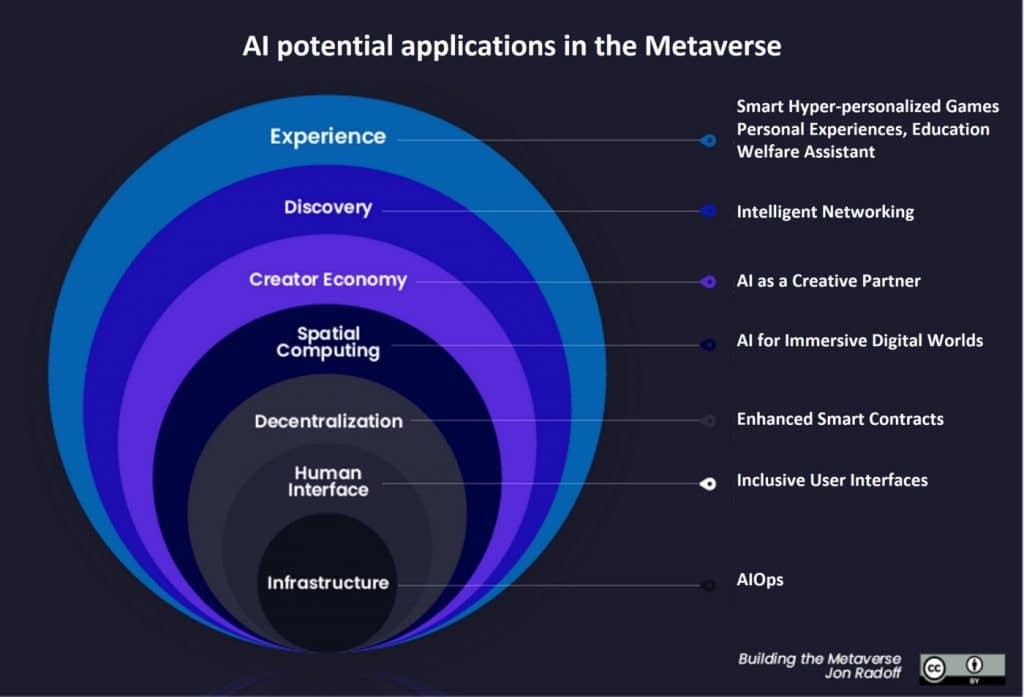
Figure: AI potential applications in the metaverse (source: towardsdatascience)
Builder Bot is Meta’s artificial intelligence technology based virtual world builder. It will have, amongst other features, a universal speech translator that will leverage natural language processing or NLP. Furthermore, meta will combine Builder Bot with its VR metaverse components and power the metaverse via its user generated data processing ability and the creation of photorealistic digital environments.
AI can also generate user avatars that resemble a user’s physical likeness making the metaverse experience more realistic. More so, AI-generated non-playing characters or digital humans could populate virtual worlds offering services such as language translation, personal assistants and watchdog services.
Other applications of AI in the metaverse include the generation of hyper-personalised experiences, smart contracts support and intelligent networking, supporting safety and inclusion for all people.
3D reconstruction
Virtual, mixed and augmented reality tools will require 3D content. To this end, 3D content creation tools are metaverse components that support extended reality. Some examples of 3D reconstruction platforms are Unity Software and the Unreal Engine.
Internet of Everything (IoE)
The Metaverse can only function via device connectivity. The Internet of Everything (IoE) connects data, people, devices and processes via private or public networks. I will feed the metaverse with data and support relevant interactions between users.
As an illustration, in the Meta announcement video, a user turns on a TV by gesturing at it. Internet of Everything (IoE) can lower device reliance on virtual assistants and voice commands.
Blockchain technology
In its future form, the metaverse could consist of open, interconnected and decentralised virtual worlds, each with its native functioning economy. Furthermore, blockchain technology will support secure and private value transfer.
It will also support immutable data storage and payment rails that allow free flow of value in a borderless space via digital currency. Distributed ledger technology will also provide the provenance of digital assets and identity via non-fungible token technology. Digital avatars are currently the hottest selling NFT class, generating over $16 billion in sales or 46% of the NFT market’s sales volume in 2021.
Conclusion
The Metaverse is the future of the internet. It will have persistence, massive scaling, interoperability and real time interactivity between its users. To achieve this feat, metaverse components such as new technologies, companies, protocols, discoveries and innovations will all come into play and merge over time, melding together to form a Metaverse.








