Intro to the P2P banking model
The advancement of technology has opened the door for new ways of delivering financial services. One of the most significant financial inventions brought by the developing technology is peer-to-peer lending (also called p2p lending, Crowdlending, marketplace lending). In the last decade, many peer-to-peer lending platforms have emerged from an unpredictable financial environment prompted by the global economic collapse of 2008. This new concept enabled small businesses and individuals to borrow money without using banks or credit unions. By this time, the banking industry was losing credibility, which was also an enabling environment for this new destructive model to thrive rapidly.
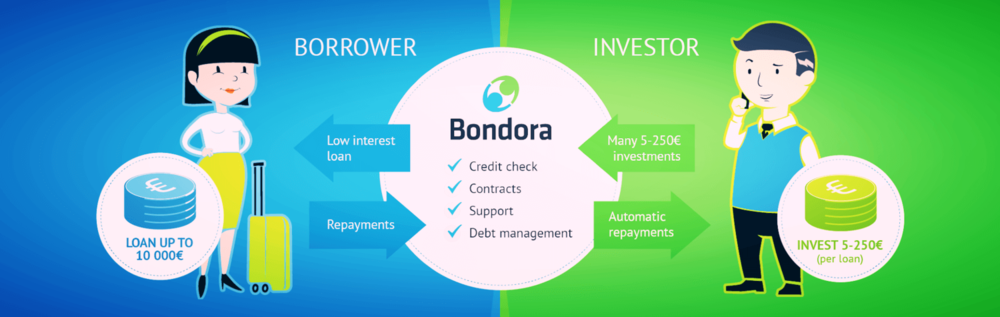
In the p2p banking model, a loan decision is based on the patented scoring and pricing structures providing a substantial amount of dealings into its fold. This essentially means that the p2p platform can also be able to cater to first-time borrowers or those who have been denied by the banks and credit unions. The creditworthiness of borrowers goes beyond just the credit scores, and sometimes borrowers may score high on other parameters other than credit score.
Lenders in the p2p system (which are the investors in this model) can also assess the eligibility of the potential borrower before deciding to fund their loan request.
The backbone of the p2p banking system is that it matches borrowers and lenders through an online platform according to their transactional approaches of ether lending or borrowing. By opening up new opportunities, p2p lending has allowed people to access credits that would otherwise not have been given by the banks due to their sketchy credit scores. In that sense, the p2p lending systems should be viewed more as a complement to traditional banks and can play a big part in the financial inclusivity by availing credit access to borrowers who are underserved by the banks and credit unions.
The difference between the P2P banking model and traditional banks
Below are some of the differences between the p2p lending model and traditional banks.
Credit Appraisal: P2P lenders look into social and payment activities of a borrower while banks treat borrowers as merely another number on the credit report. If your score is lower compared to what the banks consider acceptable, then you will be locked out. On the other hand, p2p lenders understand that each borrower is unique and cannot decide whether or not to fund the loan just on the basis of one number.
Customization: P2P lenders can provide a customized solution to borrowers based on their profile, while banks work only with standardized lending products.
Loan Approval speed: P2P lenders work with a cutting-edge technology that every step in the loan approval timeline is technologically driven. This allows reducing considerably the time of the process. On the other hand, banks takes up to 3 weeks to sanction a loan.
Loan Terms: The P2P banking model is transparent to both lenders and borrowers and both parties experience better terms and interests, which can be negotiated by lenders and borrowers.
Returns: P2P system offers investors higher returns compared to what deposits in saving accounts earn. This also due to the fact that the traditional middleman (the bank) is inexistent, thus not taking his cut.
Flexibility: In p2p lending, investors can choose from a pool of a wide range of creditworthy borrows depending on their risk appetite with terms usually varying from 30 days to 36 months.
Criteria for determining creditworthiness: This is perhaps the major difference between the p2p banking model and traditional banks. Peer to peer lending system uses a combination of factors that run through a special kind of algorithms to determine the creditworthiness of a borrower. The algorithm processes other data about the borrower in addition to their credit score. Lenders in p2p will also pull your credit report through a process called a soft inquiry. On the other hand, traditional banks simply pull your credit report and check your past history with the bank including the lines of credit, prior loan, and status of your savings or checking account.
Working Hours: In the p2p lending system, everything is done online. As an investor, you can access a p2p platform from the comfort of your home or even on the road or wherever you are. Peer-to-peer lending platforms are always open 24 hours every day. On the other hand, while most banks nowadays do have an online presence, still you will need to access the physical office to sign the papers and all that. Even if you complete your application online, you will still need to meet the loan officer physically.
Loan Auction: In p2p banking, a loan can be auctioned to other parties at a reduced rate. Bank loans or any loan for traditional financial institutions cannot be transferred to another party.
Conclusion
Perhaps the primary difference between p2p lending and traditional banks is the granted loan to the borrower. If the money is provided by a lender who is an individual, a group, or an institution, via an online platform, then that is a p2p loan. On the other hand, if the money comes from a bank, credit union or any other financial institution, then this is a bank loan.
Generally, bank loans come in the form of personal loans, while p2p loans may come in the form of business loans, consumer loans, property/real estate loans, student loans, and so on. Customers with impressive credit history stand a good chance of benefiting from bank loans due to the attractive interest rates.
Typically, interest in the p2p lending system will also be higher than in the banking system. A p2p lending loan may range from 6% to 30% APR, while a bank loan may vary from 1% to 10% APR.
[insert page=’cta-footer-crowdlending’ display=’content’]