Decentralized finance (DeFi) is one of the significant innovations in the blockchain industry. Its unique features, such as permissionless and trustless blockchain, smart contracts, etc., are attracting investors globally. The blockchain industry is growing rapidly. We come across new crypto trends almost every day. Yield farming is one of the hottest topics these days. It is among innovative applications of DeFi with several reasons to become hype.
The concept of cryptocurrency yield farming may be new to you but fear not.
In this article, you will learn what crypto yield farming is, how does it work, its benefits, leading platforms, and much more.
Let’s dig in!
What is yield farming?
Yield farming is a process of earning fixed or variable interests by lending cryptocurrencies leveraging different DeFi protocols. In other words, it is locking up cryptocurrencies as liquidity providers on decentralized platforms to earn yield such as trading fees, interest, rewards, etc.
It is one of the effective strategies to earn high profits.
In 2020, yield farming was a significant growth driver for the total funds in crypto finance. The following graph shows an exponential surge in crypto funds because of it.
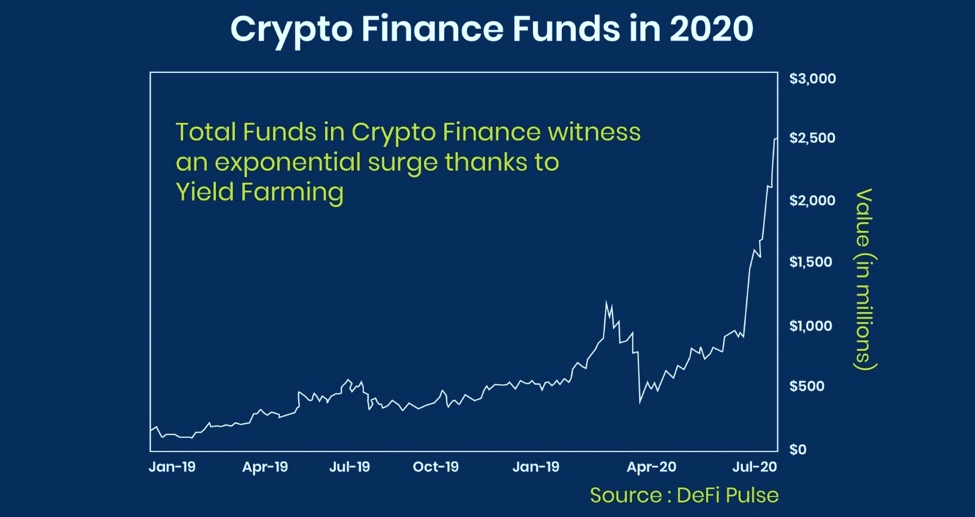
According to CoinMarketCap, on March 13, 2021, the total locked value of liquidity pools in yield farming projects was more than $13 billion.
How does yield farming work?
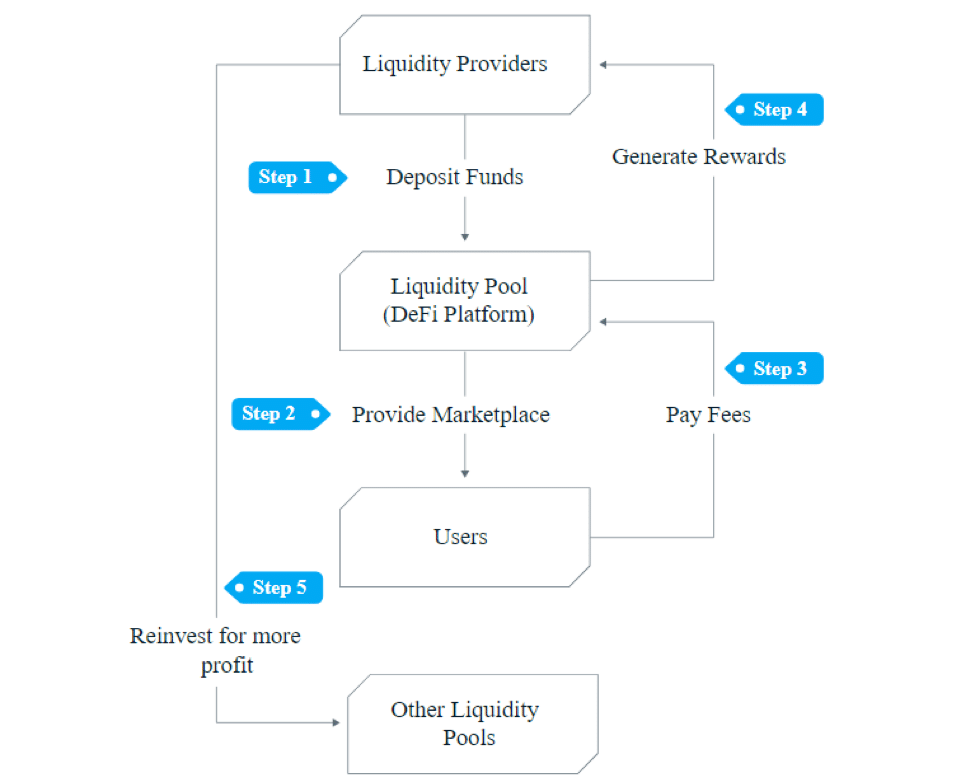
Yield farming involves liquidity providers and liquidity pools. The providers deposit funds into liquidity pools (smart contracts). This pool then powers a marketplace to enable users to carry out procedures such as borrowing, lending, and exchanging tokens. The DeFi protocols generate fees on these locked funds, which are awarded to liquidity providers in the form of yield. The amount of yield depends on their share in the liquidity pool.
The fees generated by the platform can be a fraction of transaction fees, governance tokens, or interest from lenders, etc.
Professional crypto yield farmers move their funds across multiple DeFi platforms to maximize yields to provide liquidity and earn the highest possible returns. It also allows them to diversify their assets portfolio.
The following flow chart shows the strategy of DeFi yield farming.
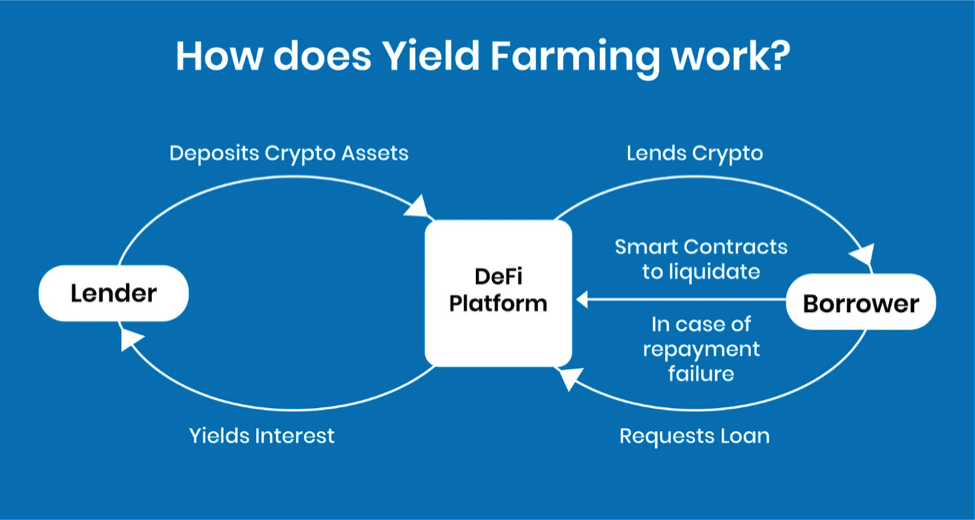
In other words, an investor (liquidity provider) approaches a DeFi platform providing yield farming opportunities to deposit his cryptos. These assets are lent to borrowers who then pay back a fixed or variable amount of interest (decided by respective platform) on investors’ loans. Interests earned by an investor are the yield.
There are certain conditions in yield farming. A borrower has to deposit double the loan amount in the form of collateral before receiving the loan. DeFi protocols involve a smart contract that tracks the value of the collateral. If the loan value is more than the collateral or the borrower fails to pay back the loan, the smart contract will immediately liquidate the collateral, paying back interests to the investor.
The following figure shows the simplified process of yield farming.
How to calculate yield farming returns?
Yield farming returns are calculated annually by some metrics such as APR and APY.
APR is “Annual Percentage Rate,” which is the amount of interest an investor earns annually. It does not involve a compounding effect which is the reinvestment of profits to generate more revenues.
APY is “Annual Percentage Yield,” which is the rate of return a lender earns on his investment. It considers the effect of compounding.
However, these metrics only provide estimations. It is challenging to calculate accurate rewards because the yield farming sector is rapidly paced along rewards fluctuations. When investors for one rewarding opportunity increase, yield returns will be reduced.
What are the benefits of yield farming?
Yield farming is prevalent because of its particular benefits. It has enormous potential to bring profits to investors. Cryptocurrency investors have earned tons of rewards from the past several months using this way. It is considered an efficient method for taking loans.
In DeFi yield farming, investors can monitor their investments using various apps via their straightforward interphase. These apps show the availability of projects for making investments. The high interoperability of DeFi platforms makes it very easy to start yield farming. Essentially, it only requires Ethereum, and a cryptocurrency wallet to start. Some DeFi protocols provide the opportunity of atomically moving cryptos across different platforms to generate higher rewards.
The following figure shows the benefits of DeFi yield farming.
What are the risks associated with crypto yield farming?
Yield farming is rewarding but sometimes can be risky for both lenders and borrowers. The following are risks associated with crypto yield farming.
Impermanent loss
In yield farming, users following the automated market markers (AMMs) lock their funds into liquidity pools to earn rewards irrespective of market fluctuations. But sometimes, there is a sudden sharp market fluctuation (if prices shift too much) in which users may suffer, losing their money. This is called impermanent loss.
The following graph shows losses to liquidity providers due to sudden market moves.
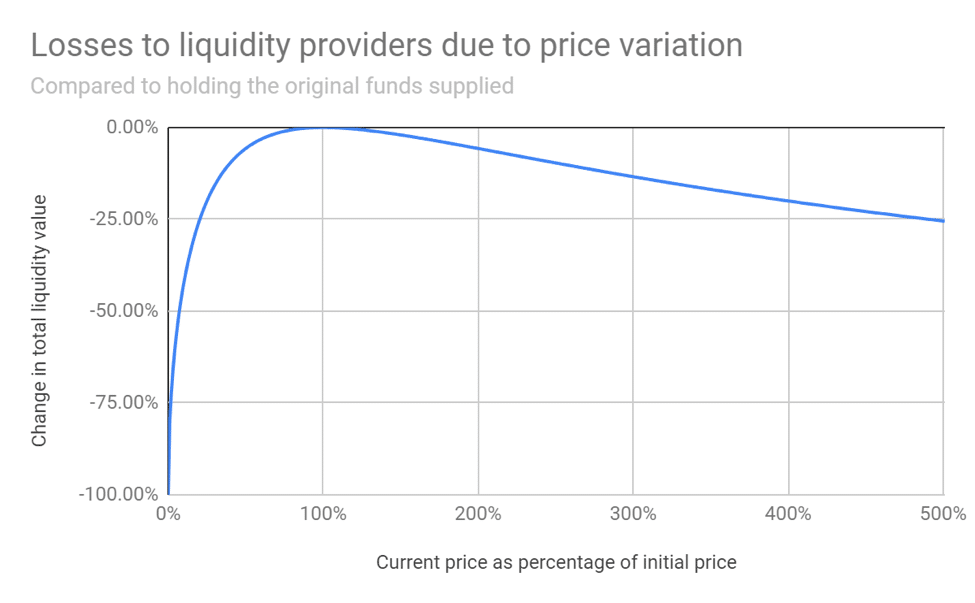
DeFi is providing great opportunities in regards, but still, there is no compact solution for eradicating this problem.
To avoid impermanent loss, liquidity providers should choose pools wisely, also consider the best timing to enter a pool. Several projects are working to provide solutions to mitigate the risk. It is also recommended to ask other users’ opinions and share their experience working with a platform.
Liquidation Risk
Liquidation happens when the value of the collateral is less than the amount of the loan. In this case, collateral is automatically liquidated (sold). A penalty is charged to the collateral when assets are sold urgently at lower prices than the market.
Liquidation risk can be reduced by using a less volatile asset. Always track the market value of both the collateral and asset. Using stable coins for both loans and collateral can also significantly reduce the risk of liquidation.
Smart contract risk
Smart contracts carry out all processes automatically according to predetermined conditions. These contracts work without human interference, therefore with negligible chances of errors. These are computer codes and developers do their best to make sure that everything works securely as intended. Still sometime, they fail to notice small errors that hackers may exploit to steal money. Even a missing semicolon (;) in the code can lead to several issues in the final project such as bugs or hacks. There are several stories when hackers drained money from smart contracts. For example, at the start of 2020, hackers stole nearly $100 million from the DeFi sector.
Ensure that your smart contract is audited, which will considerably reduce the risk of smart contract failure.
Transaction fees
In yield farming, you have to pay the gas cost to supply liquidity into a pool. It is because most of the DeFi protocols operate in Ethereum Blockchain, and gas cost at Ethereum is very high.
You can either choose to wait for commissions to decrease or may go with paying high transaction costs.
In September 2020, CoinGecko published a report of a survey conducted on yield farming. The following figure shows one of the findings of the study- farmer’s behavior in yield farming.
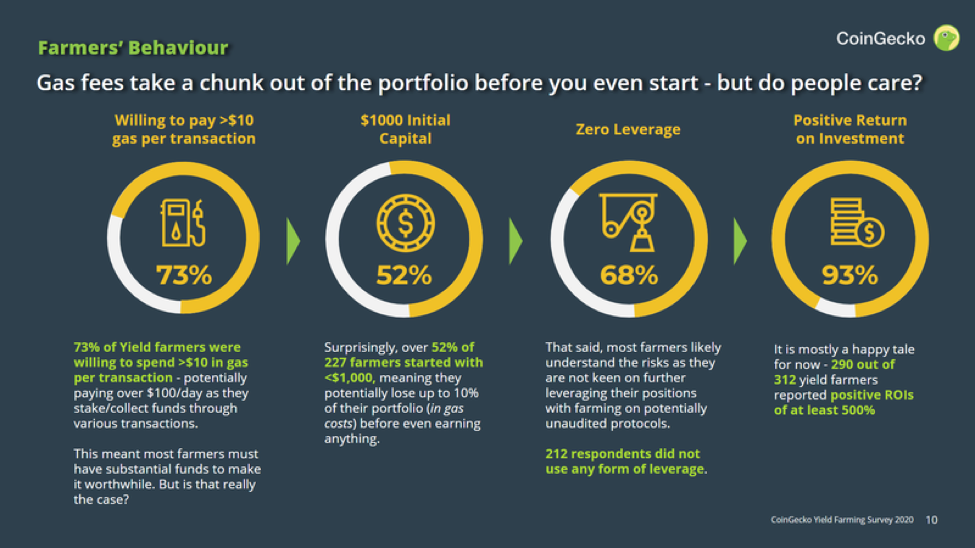
There can be other risks such as “rug pulling,” in which the developers withdraw all assets from the pools and run away with funds.
Yield farming vs. Staking

You may be confused between yield farming and staking. They may look the same to you but are different concepts. Let’s see how they are different.
Staking works on Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism in which a validator creates a block by random selection and earns rewards paid by investors. The staking rewards are directly proportional to the staking. While yield farming involves lending and borrowing, and farmers can earn multiple cryptocurrencies across several liquidity pools.
Yield farming is a complex process that generates higher rewards but is expensive. Farmers have to look for liquidity pools constantly. On the other hand, staking generates lower rewards but has fewer security risks.
Most popular yield farming platforms
There are several yield farming platforms. Each platform has its own rules and strategy along with risks. A yield farmer must know about those strategies.
The following are some of the most popular yield farming platforms.
Aave (LEND)

Aave is widely used by farmers being an open-source and non-custodial decentralized lending platform. The interest rates are adjusted algorithmically according to the market. It has a native token to reward the participants. Lenders receive “aTokens” when they contribute their funds. These tokens start earning and compounding interest immediately when deposited.
Aave also offers flash loans, making it an attractive option for investors.
Compound Finance (COMP)

Compound is one of the main protocols of yield farming. It is an algorithmic money market that enables users to borrow and lend assets. Users having an Ethereum wallet can supply assets to a liquidity pool of Compound and earn rewards that start compounding immediately. The rates are updated algorithmically depending upon market supply and demand. The platform ensures high-level security and is audited.
Curve Finance (CRV)

Curve Finance is an Ethereum based DEX liquidity protocol built especially for efficient, stable coin swap. It allows users to exchange stable coins charging a low fee and with low slippage. It also allows swift trading between USDC, TUSD, and BTC.
Uniswap (UNI)

Uniswap is a widely famous decentralized exchange protocol that allows trustless swaps of almost all ERC20 token pairs. It provides an opportunity for automated transactions on the Ethereum blockchain using smart contracts.
Liquidity providers must stake both sides of the liquidity pool in a 50/50 ratio. In return, they earn a portion of transaction fees and UNI governance tokens. Uniswap is a growing protocol with two versions V2 and V3.
PancakeSwap (CAKE)

PancakeSwap is based on Binance Smart Chain, which uses an AMM model where users can trade against a liquidity pool. The main focus of PancakeSwap is on games with a lottery, NFT collectibles, etc.
Yearn. Finance (YFI)

Yearn.Finance is another automated DeFi protocol that algorithmically allows yield farmers to seek the most profitable yield farming services. It allows using lending protocols such as Aave and Compound for maximizing profits.
Balancer (BAL)

Balancer is a multi-token AMM protocol that distinguishes itself through flexible staking. Liquidity providers can establish customized Balancer pools to carry out trading with varying token ratios and earn fees.
Synthetix (SNX)

Synthetix is a synthetic protocol that supports any commodity with a reliable price, such as gold, silver, cryptocurrencies, etc. Users can also lock up the platform’s native token SNX as collateral to mint synthetic assets against the token.
Total supply and APR comparison of yield farming platforms
The following table compares the total supply and APR values of the above-mentioned yield farming platforms in August 2021.
Protocol | Total Supply | APR / APY |
Aave | $21 billion | Up to 15% APR |
Compound Finance | $16 billion | 0.21% to 3% APY |
Curve Finance | $9.7 billion | 10% APY |
Uniswap | $2-5 billion | ∼17% APY |
PancakeSwap | $4.9 billion | 400% APY |
Yearn.Finance | $3.4 billion | 80% APY |
Balancer | $1.8 billion | 43% APY |
Synthetix | $234 million | ∼34% APY |
Figure: Total Supply and APR comparison of yield farming protocols as per values in August 2021.
Best practices in yield farming
If you have decided to go into yield farming, the following practices may prove to be beneficial.
- Always use the native coins such as ETH, BNB, etc., and stable coins such as USDT, USDC, etc., at the start to generate new tokens. Working with new tokens at the opening may cost you a lot with a small liquidity pool.
- Farming a paired pool may lead to impermanent loss or scams so, it is recommended to calculate the risk before.
- If you prefer to get your principal funds, leaving only the profit in the pool to generate more profit, can save your funds from any mishap.
- Re-farm your profit tokens in a single pool to generate higher yields.
- Daily monitor the market and switch to other protocols if it makes sense.
- Do not over-borrow because something that works for others may not work for you.
- Make yourself well familiarized with the risks.
- Do proper research before making any decision.
- Always use a reputed platform.
Conclusion
Crypto yield farming is new within the DeFi infrastructure but is quickly growing. It has the potential to incentivize liquidity and enable the fair distribution of tokens. It has significantly reduced slippage for token swap, bringing considerable benefits to DeFi stakeholders.
Yield farming is expected to have a bright future bringing new advancements. But as it is complex and risky, therefore, you must have a proper understanding before stepping into this sector.
Keep yourself updated with market moves, and never hesitate to learn more. Stay tuned for the next article.








